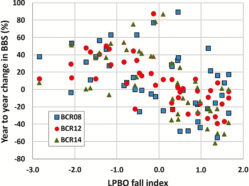
Winter Experiences Carry Over into Swallows’ Breeding Success
There’s no shortage of studies demonstrating that conditions during one part of birds’ annual of breeding and migration cycle can affect individuals in subsequent stages — a phenomenon known as carry-over effects.